Information contained in three studies published in the journal Sciences Compiled from recordings of ten earthquakes detected on the surface of Mars.
This is the first exploration by seismology of the internal structure of a terrestrial planet other than Earth and an important step in understanding the formation and thermal evolution of Mars.
The scientists explained in a press release.
The internal structure of Mars is still poorly understood to this day. The models were based solely on measurements collected by Earth-orbiting satellites or on analysis of Martian meteorites that have fallen to Earth.
Explain the researchers.
So far, the thickness of Mars’ crust has been estimated between 30 kilometers and 100 kilometers and the radius of its core ranges between 1,400 kilometers and 2,000 kilometers. The internal structure of the planet and the depth of the boundary between the crust, mantle and core remain unknown.
Thanks for posting InSight mission to Mars in early 2019Expedition scientists have collected and analyzed seismic data for two years.
On Earth, it usually takes more than one seismic monitoring station to determine a structural model, the time of arrival of an earthquake, and its aftermath.
Since the scientists only had one station on Mars, they had to search for, identify and validate the signature of waves that interacted differently with Mars’ internal structures in seismic records.
These new measurements, along with metallurgical and thermal modeling of the internal structure, made it possible to overcome the limitations of the single station. A method that opens a new era for planetary seismology
, outlines the press release.
The collected information was processed daily and cleaned of ambient noise (wind and distortion associated with rapid changes in temperature).
Scientists have recorded more than 600 seismic events, more than 60 of which correspond to relatively distant earthquakes.
About ten of these earthquakes contained deep structure information.
The direct seismic waves of an earthquake are somewhat similar to the sound of our own voice in the mountains, which generates echoes. And it is the echoes of these waves, coming from a reflection on the nucleus, on the interface of the crust or even on the surface of Mars, that we looked for in the signals thanks to their similarity with direct waves.
Explains Philippe Lugnona of the Institute of World Physics in Paris.
Milestones
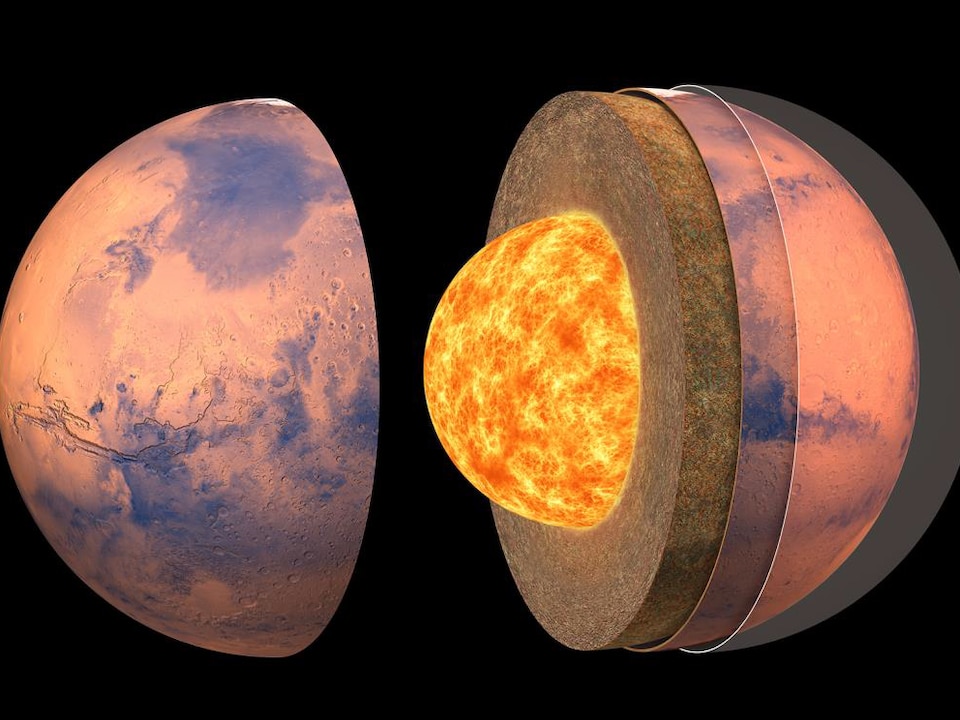
Like Earth, Mars formed from dust and meteorite clusters of material orbiting the sun that helped shape the beginnings of the solar system. During its first tens of millions of years, the planet split into three distinct layers: the crust, the mantle, and the core.
internal structure
The behavior of seismic waves, passing through the crust before reaching the Insight station, made it possible to identify several discontinuities in the crust:
- The first (observed at a depth of about 10 km) indicates the separation between a highly variable structure, resulting from a very old circulation of fluid, and a slightly altered crust.
- The second discontinuity, about 20 km, and then the third less pronounced, about 35 km, reveals the stratification of the crust.
In the mantle, the differences between the travel time of the waves generated directly during the earthquake and that of the waves generated during the reflection of these direct waves at the surface were analyzed. These differences make it possible, with a single station, to determine the structure of the upper mantle, and in particular the variation in seismic velocities with depth. However, these differences in speed are related to temperature.
This allows us to estimate Mars’ heat flux that would be three to five times weaker than Earth’s, and issue constraints on the composition of Mars’ crust that would concentrate more than half of the radioactive elements. Heat producers on the planet
Adds French Henri Samuel, also from the Institute of World Physics in Paris.
liquid heart
Scientists also searched for waves reflected from the surface of the Martian nucleus, whose radius is one of the main results of the InSight mission
.
Despite the low amplitudes of the signals associated with the reflected waves, an excess of energy was observed for a core with a radius between 1,790 km and 1,870 km. This size indicates the presence of photonic elements in the liquid core and has serious consequences for mantle minerals at the mantle/core interface.
, explains Melanie Drillo, engineer at the Higher Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics in France.
still questions تزال
Thus, these three studies make it possible to draw a first model of the internal structure of the planet up to the core. Thus Mars joins Earth and the Moon in the club of planets and satellites whose deep structure is being explored by seismology.
Scientists rejoice.
But this new data also raises questions: Is crustal weathering over the first 10 kilometers general or limited to the InSight landing zone? What will be the impact of these early models on theories of thermogenesis and the evolution of Mars, especially in the first 500 million years when Mars had liquid water on its surface and powerful volcanoes?
InSight’s mission has been extended for two years, a period that will allow for the collection of new information that may answer these questions.

“Proud thinker. Tv fanatic. Communicator. Evil student. Food junkie. Passionate coffee geek. Award-winning alcohol advocate.”